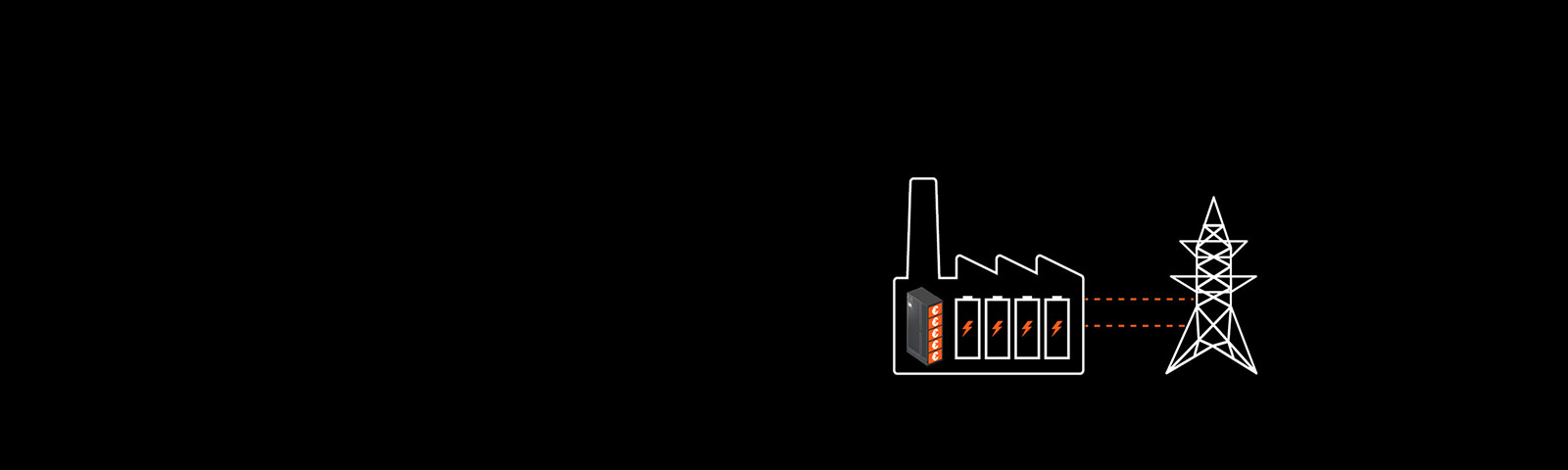
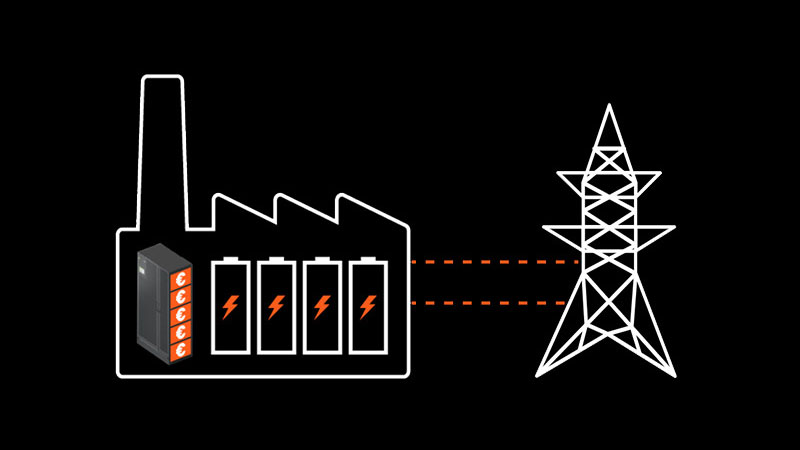
Last month, I was delighted to participate in a spirited roundtable discussion with several colleagues on the topic of grid scale and how data center operators can participate in what is called “grid service interaction.” What this means is data center and other critical infrastructure organizations leveraging battery and Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems with Dynamic Grid Support technology to interact with and balance the grid during periods of instability.
The decommissioning of large power plants and the intermittency of renewable sources of energy that feed the grid are examples of such events. Providing Dynamic Grid Support can unlock a number of benefits, including costs savings, improved operational resilience, and even new revenue generation opportunities.
Following our discussion, here is a brief outlook on the technology behind UPS systems with Dynamic Grid Support, how it works, what are the challenges and benefits, and how Vertiv can support operators through the use of these and other smart assets
What’s Driving the Industry’s Next Potential Power Move
The data center industry is at the center of the world’s relentless demand for more energy and corresponding push for more renewable sources that reduce carbon emissions. Industry stakeholders are looking for solutions that address the grid stability risks posed by surging demand and the momentary imbalances common to renewable energy sources – a trait that can lead to frequency variations and, if unchecked, outages.
What makes a UPS or other energy storage systems strong candidates for grid balancing is that backup batteries in a UPS only come into play should an outage occur, meaning these batteries spend much of their lifetime unused. Smart UPS technology uses the batteries’ storage systems to accumulate energy and instantly release it whenever needed —without hindering the UPS system’s ability to protect the load. Additionally, a grid-interactive UPS with a properly sized energy storage system is designed to provide a fast enough response to meet the needs for frequency containment and support income-generating services.
Grid Balancing Basics
A grid-interactive UPS must be capable of powering ancillary services while maintaining sufficient battery runtime to allow for normal transfer to generators in the event of a utility failure.
When the external controller detects a grid frequency variation, it commands the UPS to follow this request for positive and negative regulation by charging or discharging the batteries within their operational limits. The UPS controls the input power to achieve certain targets or services by working in a variety of different modes.
Examining the Revenue and Balancing Potential for End Users
A grid interactive UPS can enable businesses and private energy users to commercialize the energy they store and lower overall energy costs. This is done through balancing services, which help demand meet grid supply by targeting fast frequency response and demand management. Balancing services guarantee the power supply matches the actual demand, ensuring the stability of the grid and allowing for both revenue generation and energy savings.
In fast frequency response service programs, the UPS battery storage systems are used to amass energy and release it instantaneously. Alternatively, demand management, known also as “peak shaving,” is a balancing approach that reduces grid reliance in times of power scarcity or high energy costs. Demand management services are offered through programs, in which companies receive a regular financial payment based on the size of the contract for such services. One example is a priced-based program where consumers adjust their energy consumption according to the changes in electricity market price. Another is an incentive-based program where earnings are provided through contracts where consumers are paid to shift or reduce their energy consumption.
Data center organizations offering grid balancing services receive additional “energy” payments based on how quickly they react to grid frequency variations, as well as on the amount of energy reduced.
Remaining Challenges to Overcome
During our discussion, we talked about some of the barriers of adoption that remain for incorporating grid scale technology. This technology remains relatively new and years away from mainstream adoption, so there is understandable hesitancy about making significant changes to UPS technologies customers rely on to protect their critical systems. There also are concerns as to whether this grid support technology will affect the resiliency of the UPS or cause the batteries to age or degrade faster.
These concerns are unfounded. The control system on the UPS has the ability to pause/exit Dynamic Grid Support mode when the operating conditions are out of specification or increase risk. Additionally, leading UPS systems are designed with optimization features, advanced diagnostics, and lithium-ion battery storage to control the main aging factors and increase the life of the battery.
Despite the skepticism, a recent survey from OMDIA, an analyst and consultancy firm, offers a positive outlook for adoption. According to the survey, about 90% of data center operators are likely to deploy UPS systems to interact with the grid and support essential energy management initiatives within the next four years. For some organizations, the move toward adoption may rely on seeing more of the major data center players using the technology and observing how it matures over time. Regardless, as we see more effort to stabilize the grid and move away from traditional energy sources, few will be able to ignore the benefits a grid interactive UPS provides.
Vertiv has the capabilities to support operators in generating revenue and reducing costs by offering smart assets such as UPS systems with grid support functionalities. We also can supply the full integrated solution (grid Interactive UPS with external controller and energy storage) both to the end user and the aggregator/energy service provider. To learn more about this technology and how Vertiv can help your organization take advantage of these savings opportunities, download our white paper, “How to Maximize Revenues from Your Data Center Energy Storage System with Grid Interactive UPS.”