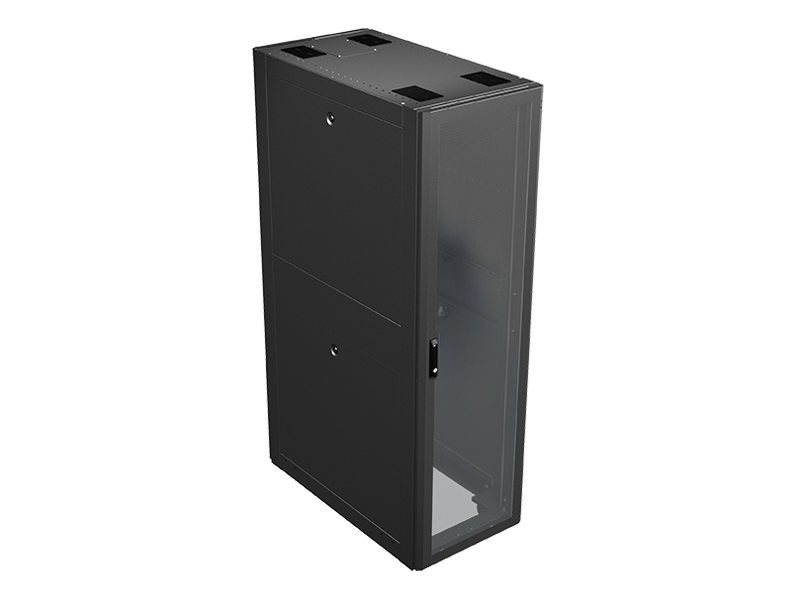
IT racks play an integral part in data center availability and reliability. They can enhance the efficiency of supported equipment and improve the productivity of the data center personnel.
Choosing the right IT rack need not be a daunting task. It starts with assessing your organization’s priorities. Understanding the most salient factors eases decision-making. Each organization has its own primary consideration, for example, one may choose IT racks that are most cost-effective while another organization may opt for IT racks that are scalable to meet their growth plans.
As IT requirements continue to evolve, so do IT rack designs. Not only are IT racks required to provide protection and secure access to critical IT resources, they are expected to adapt to accommodate data center changes. Any purchase today should be considered an investment for tomorrow. So, the basis of selection should not just be the least expensive today but those with flexibility to deliver reliability and lower total cost of ownership over time.
IT Rack Essentials
IT racks, sometimes called server racks, LAN racks or network racks, hold critical IT systems and accessories that support the operations. The rack-mounted or rack-mount devices are the IT equipment bolted or clipped to the rack such as UPS or network switches.
The IT rack size is determined by the type and quantity of the rackmount device and measured by a rack unit (U or less commonly called RU), which is the vertical space available in an IT rack. It is applied to the IT racks themselves as well as the devices inside. It is standardized as multiples of 1.75 inches (44.45 mm) or one rack unit or “U”. Most IT racks are sold in the 42U form, which means a single rack can hold forty-two (42) 1U devices, or any combination of 1U, 2U, 3U or other rack unit heights that add up to 42 or less. Standard-sized IT racks are the usually chosen because they can fit standard-sized components.
The 19-inch IT rack is the standardized size frame or enclosure for mounting equipment specified in the EIA-310E of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). This is widely used for computer server equipment. This allows dense hardware configurations in space-saving enclosure.
Types of IT Racks
There are various IT rack types in the market, with their respective pros and cons. Determine what the IT equipment and accessories would be mounted in the IT racks as well as their requirements, then see what rack type would fit them best.
Preconfigured or Customized
Pre-configured IT racks are factory-assembled and shipped. They are often the less expensive option.
The customized IT racks are designed to meet customers’ unique rack needs and specifications such as width, height, depth, water or dust proofing, or shock resistance. Customers usually provide their own specifications and drawings and work closely with the provider to receive custom IT rack solutions.
Learn about Vertiv Preconfigured IT RacksOpen frame or Enclosed
IT racks can also be open frame or enclosed (closed cabinet). Open frame IT racks have more space and flexibility, allowing more accessibility. Though they are cheaper, they are more prone to security issues. They are also more exposed to dirt and dust. Since they are not locked, they are often found inside secure server rooms.
Usually more expensive, closed IT racks can be locked. Closed racks are a better option if the IT rack will be placed outside a secure server room or in a nonsecure location.
Selecting the IT Racks
As today’s data centers continue to evolve, IT racks should be able to adapt to changes. Consider IT racks that can be flexible and adaptable in these key areas.
Weight capacity
1U servers weigh approximately 15 kg. Usually, a rack with a 1000 kg capacity should be considered in a typical data center given the number of servers, cables, rack power distribution units, overhead cable mounts and containment support required today. Racks are available in up to 1500 kg capacities for heavy-duty applications.
19-inch rails
Each of the four rails in a rack should be easy to adjust relative to the needs of the supported equipment. Proper alignment ensures that rails are properly positioned without the need to measure. Front rails should also be flexible to allow for cables in a networking application. Rails that utilize cage nuts eliminate the need for tapping and drilling out stripped screw holes. Stripping out a hole is easy; repairing it is time consuming, and therefore expensive. Cage nuts are available in a variety of sizes, attach to the rail wherever necessary, and provide an economical, fast and flexible method of mounting.
Doors
Most vendors offer doors with approximately 60-80 percent perforation for proper air flow (higher perforation levels improve airflow capability). The doors should also be easily reversible with lift-off hinges that require no tools to change the door’s configuration to open from either the right or left. Doors that can be easily removed from their hinges simplify equipment loading. Some doors offer the ability to open 160 degrees and more, which also eases equipment loading. There are numerous handle options, such as key locks, combination, electronic or biometric locks, all of which are built into the handle.
Grounding
All components, including the roof, doors, rails, side panels and frame should be grounded for safety. They should also be easily disconnected for convenience. For instance, should a door need to be removed for reversal, a quick-disconnect grounding wire will speed the process. A central grounding point that connects to the building’s central ground should also be used.
Learn more about IT rack trends and selection Learn more about Vertiv IT Rack SolutionsIT Rack Security
Security is another top concern for data center managers. Measures are being taken to safeguard data from online threats as well as physical threats. IT racks with lockable side panels and doors can prevent unwarranted access or theft.
All racks should be either bayed (attached) together, bolted to the floor or utilize an anti-tip device for safety purposes. If a 19-inch piece of equipment would be partially removed from a rack for service, it can make a rack top-heavy and unstable (if not weight-balanced from below) and create a safety hazard. The least expensive way to achieve stability is baying. Anti-tip devices are installed on the front of the rack and provide a set of legs that may be pulled out when rack components are being serviced, expanding the footprint of the rack’s base. Physical security may also be required in an area of high seismic activity since IT racks must be stable to survive potential earthquakes.
IT Rack Cooling
Organizations need efficient and reliable heat management and humidity control solutions geared to their specific size, location and business goals. Environmental and economic issues are driving businesses to get energy efficient, environmentally friendly solutions in their data centers. With thermal management systems, they can improve protection of their data centers and critical IT spaces, while ensuring low operating costs and enhancing their revenue potential.
Select thermal solutions that are self-optimizing, rapidly deployable and meet IT challenges and demands. Find scalable, space-saving solutions for the rack densities applicable to data center needs.
Learn more about Vertiv Thermal Management SolutionsIT Rack Accessories
IT racks require various accessories to run effectively. Tool-less options allow for quick installation and configuration. The common IT rack accessories are:
- Cable Management
- Airflow Management
- Shelves and Supporting Brackets
- Anchoring
- Single Perforated Doors
- Side Panels
- Server Rails
- PDU-Cable Management Brackets
- Top Panels
Cable Management
While densities under 10kW per rack remain the norm, deployments at 15 kW are typical in hyperscale facilities – and some are even gearing 25 kW. High density configurations allow improved levels of performance and capacity but also increase cabling density.
As more power is delivered to more circuits within a rack, additional required cables create obstructions within the rack, which can make heat removal more difficult. Data center managers must position and route cabling correctly and provide ready access to equipment.
Optimized cable management can enhance system availability and improve your bottom line. Proper cable management can reduce signal interference, improve maintenance and serviceability, enhance cooling efficiency and provide scalability and adaptability. However, improper cable management can result in cable damage and failure. This can lead to data transmission errors and performance issues as well as system downtime.
Learn more about proper cable managementAirflow management
With higher heat loads, higher levels of cabinet door perforation are needed to maximize airflow. Airflow management peripherals can optimize efficiency. Tool-less blanking panels offer a useful option from an energy efficiency standpoint. Blanking panels may be added to any unused U space, to ensure that hot-aisle air is not drawn back into the cold aisle. Vertical airflow baffles should be considered for cabinets wider than 600 mm, to prevent short cycling of air and maintain the hot-aisle/cold-aisle advantage.
IT Rack Deployment
Today’s IT racks offer features that improve equipment installation speed. Tool-less installation allows adding new equipment or changing configurations even at a moment’s notice. This makes equipment mounting a fast “slide in, slide out” procedure that saves time and labor during deployment.
Data center managers are realizing the advantage of using a single manufacturer for integrated and complementary solutions. These solutions that bring together related hardware, software, and services to enhance efficiency, reduce cost and allow for fast and easy deployment.
Futureproof IT Racks
IT racks can ensure the optimal environment for the IT equipment. They should adapt to data center and provide options for scalability, flexibility and adaptability. Choosing the right IT racks and configuring them to match your business needs will ensure IT equipment will operate reliably and efficiently. In contrast, failure to properly design and deploy IT infrastructure can lead to underutilized systems, stranded capacity and higher operating costs, preventing organizations from gaining the full advantage of the data center.



